-
Scoliosis
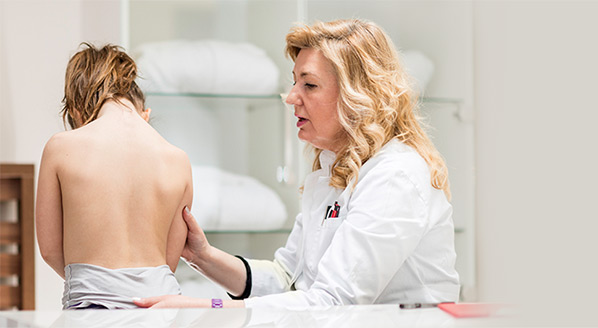
Scoliosis is a condition characterized by the abnormal curvature of the spine. This occurs secondary to a 3 dimensional deformity of the spine.
-
Pediatric Spine
The spine in a growing child is unique. Growth of the spine is linked to growth of the chest, lungs and other internal organs.
Certified by the American Board of Orthopedic Surgery, Dr. Younas specializes in orthopedic care for infants, children and teens with an emphasis in spinal deformities and scoliosis.
MeetShiraz Younas, M.D.Pediatric Orthopedic and Scoliosis Surgeon
Dr. Younas was named to Houstonia magazine’s listing of Top Doctors in Houston in 2014 and was selected by his peers as a Texas Super Doctors Rising Star in 2015. He is the coauthor of original articles published in peer-reviewed journals, including Arthroscopy, Orthopedics, American Journal of Sports Medicine, Foot and Ankle International and Journal of Pediatric Orthopedics.
Scoliosis & Spinal
Deformity Conditions
Scoliosis is a condition characterized by the abnormal curvature of the spine that causes a deviation to one side. It causes a physical deformity
-
5420 West Loop South, Suite 2300
Bellaire, Tx 77401- Tel:
-
950 Corbindale Rd, Suite 300,
Houston, TX 77024 -
17520 West Grand Parkway South, Suite 200,
Sugar Land, TX 77479 -
23910 Katy Freeway, Suite 201,
Katy, TX 77494 -
27700 Northwest Freeway, Suite 200,
Cypress, TX 77433













I am very happy with my child's provider. *Dr. Younas and also [...], help us to understand the ...