- Conditions
- Procedures
Casting for Nonoperative Fractures
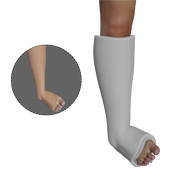
Casting and splinting are the commonly rendered non-surgical treatment options for injuries related to the bones and soft tissues (muscles, tendons, ligaments). Casting and splinting help stabilize fractures and reduce pain, swelling, and muscle spasm.
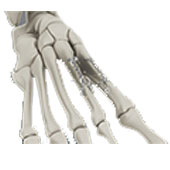
Internal Fixation of Fractures
Foot and ankle fractures are breaks or cracks in any bone of your foot and ankle joint. Fixation of fractures is a surgical method of reconnecting the broken or cracked bones and fixing them in the correct place using orthopedic hardware.
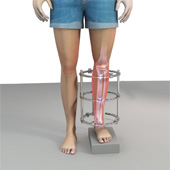
Limb lengthening
Limb lengthening is a reconstructive procedure where the deformed bone is straightened or missing bone is replaced. It is performed in children and adults who have variations in their leg length because of a disease, injury or birth defect. The limb lengthening procedure can be performed by minimally invasive techniques.
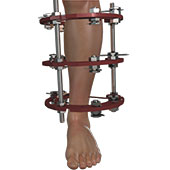
External Fixator Assisted Limb Deformity Correction
Foot and ankle fractures are breaks or cracks in any bone of your foot and ankle joint. Fixation of fractures is a surgical method of reconnecting the broken or cracked bones and fixing them in the correct place using orthopedic hardware.
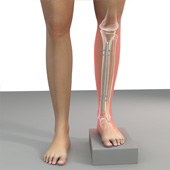
Internal Lengthening for Leg Length Discrepancy
Limb lengthening is a reconstructive procedure where the deformed bone is straightened or missing bone is replaced. It is performed in children and adults who have variations in their leg length because of a disease, injury or birth defect. The limb lengthening procedure can be performed by minimally invasive techniques.
Pediatric Orthopedic Surgery
Surgery performed to treat orthopedic conditions in children and adolescents is called pediatric orthopedic surgery. Orthopedic problems in children are different from that of adults as the bones in children are constantly growing and are bendable until a certain age. Moreover, young children may not be able to express the symptoms associated with bone or joint conditions to their physicians.